CH02-ArrayList
概述
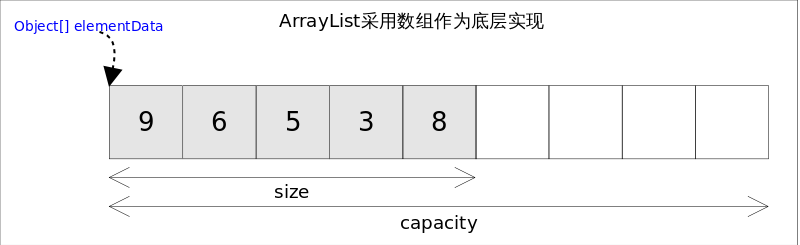
- ArrayList 实现了 List 接口,是顺序型容器,允许 NULL 元素,底层结构为数组。
- 除了没有实现线程安全,其余实现与 Vector 类似。
- 拥有容量(capacity)属性,表示底层数组大小,实际元素个数不能大于容量。
- 容量不足以承载更多元素时,会执行扩容。
- size、isEmpty、get、set 均可在常数时间内完成。
- add 的时间开销与插入位置有关。
- addAll 的时间开销与所要添加元素的个数成正比。
- 其余方法大多为线性时间。
内部实现
数据结构
transient Object[] elementData;
private int size;
构造函数
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // 10
}
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
自动扩容
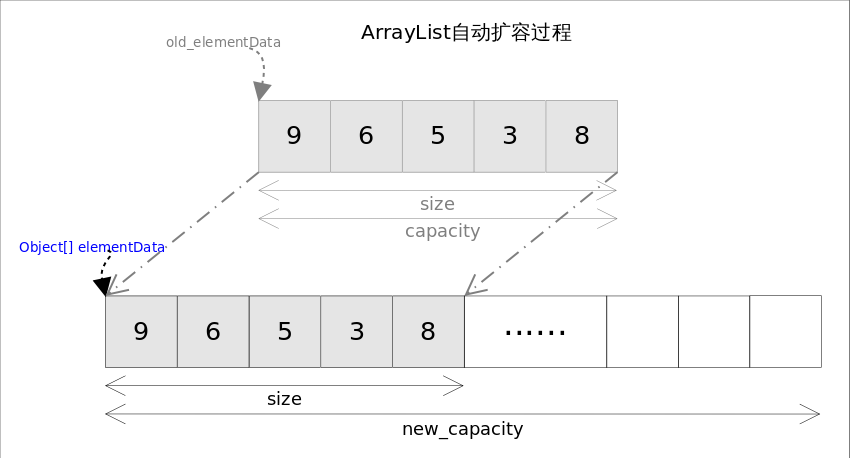
每当向数组中添加元素时,都要去检查添加后元素的个数是否会超出当前数组的长度,如果超出,数组将会进行扩容,以满足添加数据的需求。数组扩容通过一个公开的方法ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)来实现。在实际添加大量元素前,我也可以使用ensureCapacity来手动增加ArrayList实例的容量,以减少递增式再分配的数量。
数组进行扩容时,会将老数组中的元素重新拷贝一份到新的数组中,每次数组容量的增长大约是其原容量的 1.5 倍。这种操作的代价是很高的,因此在实际使用时,我们应该尽量避免数组容量的扩张。当我们可预知要保存的元素的多少时,要在构造ArrayList实例时,就指定其容量,以避免数组扩容的发生。或者根据实际需求,通过调用ensureCapacity方法来手动增加ArrayList实例的容量。
/**
* Increases the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
add/addAll
添加单个元素的方法 add(E e) 和 add(int index, E e),在执行之前都需要检查剩余容量,如果需要则自动扩容,即执行 grow 方法。
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
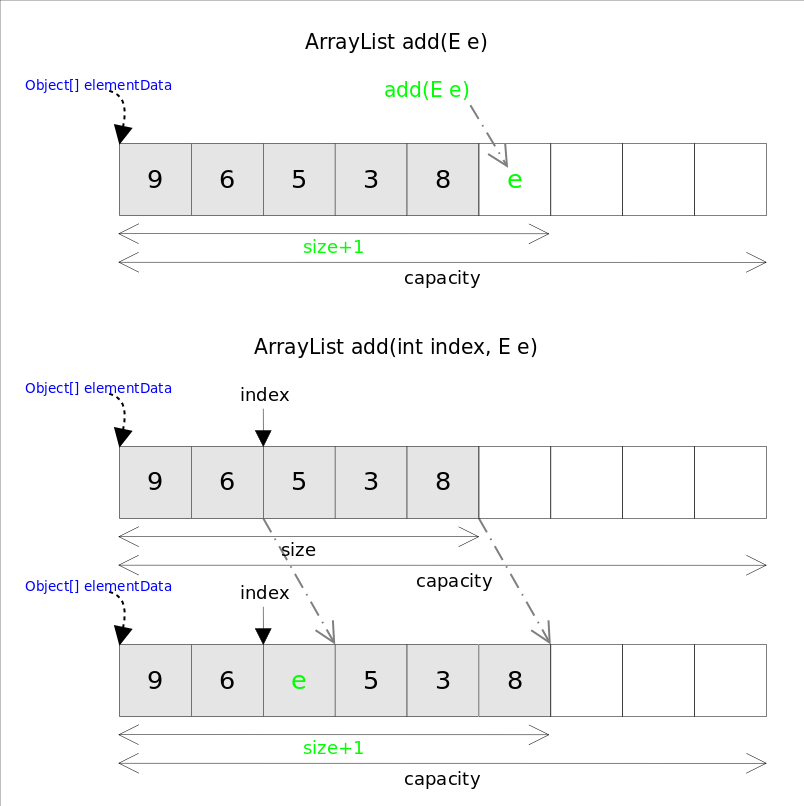
add(int index, E e) 首先需要移动元素,然后完成插入操作,因此具有线性时间的复杂度。
addAll() 能够一次添加多个元素,根据添加的位置拥有两种版本的实现:
- 向末尾添加:
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) - 向指定位置添加:
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
在插入之前也需要扩容检查,如果需要就执行扩容。如果插入指定位置,也需要移动元素。因此同时与插入元素的数据和插入的位置相关。
set
首先执行越界检查,然后对数组指定位置的元素赋值。
get
首先执行越界检查,然后数组指定位置的元素值,最后转换类型。
remove
remove(int index)删除指定位置的元素remove(Object o)删除第一满足 equals 条件的元素
remove 是 add 的逆操作,需要将删除位置之后的元素向前移动。
为了让 GC 起作用,必须显式的为最后一个位置赋值为 null,即解除引用。如果不设为 null,那么该位置将会继续引用原有的对象,除非被一个新的对象覆盖。
trimToSize
该方法可以将数组的容量调整为当前实际元素的个数。
/**
* Trims the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
indexOf, lastIndexOf
分别获取第一次和最后一次出现的元素位置:
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
fail-fast 机制
通过记录 modCount 的值,在面对并发修改时,迭代器很快就会完全失败,避免在将来某个不确定时间发生任意不确定行为。
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.