CH06-7-原型模式
原型模式是一种从已存在的对象创建新对象的创建型模式。其目的在于避免昂贵的调用来保持高性能。
类图
在 Java 语言中,我们通常会看到一个类实现一个带有clone方法的接口,它返回一个该类的新实例。限免的图示展示了其类图:
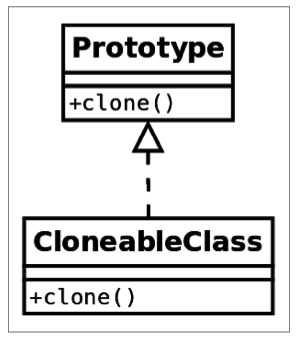
实例
Scala 中原型模式的实现变得尤其简单。我们可以使用一种语言特性。由于原型设计模式真的类似于生物细胞分裂,让我们用一个细胞作为一个例子:
/** Represents a bio cell */
case class Cell(dna: String, proteins: List[String])
在 Scala 中,所有的 case 类都拥有一个copy方法,它会返回一个克隆自原有实例的新实例。并在复制的过程中改变一些值。下面是用法:
object PrototypeExample extends App{
val initialCell = Cell("abcd", List("protein1", "protein2"))
val copy1 = initialCell.copy()
val copy2 = initialCell.copy()
val copy3 = initialCell.copy(dna = "1234")
System.out.println(s"The prototype is: ${initialCell}")
System.out.println(s"Cell 1: ${copy1}")
System.out.println(s"Cell 2: ${copy2}")
System.out.println(s"Cell 3: ${copy3}")
System.out.println(s"1 and 2 are equal: ${copy1 == copy2}")
}
优点
当性能很重要的时候原型模式将会很有帮助。使用copy方法,我们不用花费时间创建就能得到实例。缓慢可能源自一些创建过程中引起的计算,必须数据库调用或数据查询,等待。
缺点
使用对象的浅(shallow)拷贝可能引起错误或副作用,实际的引用会指向原始的实例。同时,避免构造器可能导致烂代码。原型模式需要被真正的用于不使用则会引起巨大的性能影响的场景。
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.