CH04-运行配置解析
在 Spring 与 MyBatis 的集成中,通常需要声明一个 sqlSessionFactory 用于初始化 MyBatis:
<!-- 注册 sqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:config/mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.wch.base.domain"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
在 bean 初始化的时候会调用 SqlSessionFactoryBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法,在此方法中 MyBatis 使用 XMLConfigBuilder 对配置进行解析。
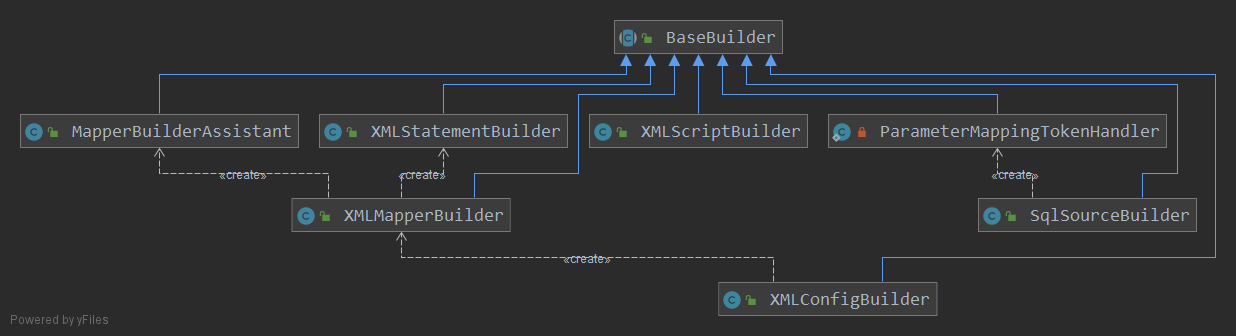
BaseBuilder 体系
XMLConfigBuilder 是 XML 配置解析的入口,继承自 BaseBuilder,其为 MyBatis 初始化提供了一系列工具方法,如别名转换、类型转换、类加载等。
全局配置对象
XMLConfigBuilder 在构造方法中创建了 Configuration 对象,这个对象中用于保存 MyBatis 相关的全部配置,包括运行行为、类型容器、别名容器、注册 Mapper、注册 statement 等。通过 XMLConfigBuilder 的 parse 方法可以看出,配置解析的目的就是为了获取 Configuration 对象。
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
// 创建全局配置
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
// 设置自定义配置
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
// 解析标志
this.parsed = false;
// 指定环境
this.environment = environment;
// 包装配置 InputStream 的 XPathParser
this.parser = parser;
}
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 读取 configuration 元素并解析
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
解析配置文件
配置解析分为多步,详情可参考 XML 配置。MyBatis 源码内置 mybatis-config.xsd 文件用于定义配置文件书写规则。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
// 解析 properties 元素
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 加载 settings 配置并验证是否有效
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
// 配置自定义虚拟文件系统实现
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 配置自定义日志实现
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
// 解析 typeAliases 元素
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析 plugins 元素
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析 objectFactory 元素
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 解析 objectWrapperFactory 元素
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 解析 reflectorFactory 元素
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
// 将 settings 配置设置到全局配置中
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析 environments 元素
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析 databaseIdProvider 元素
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析 typeHandlers 元素
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析 mappers 元素
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
解析 properties 元素
properties 元素用于将自定义配置传递给 MyBatis,例如:
<properties resource="com/wch/mybatis/config.properties">
<property name="username" value="wch"/>
<property name="password" value="Noop"/>
</properties>
其加载逻辑为将不同配置转为 Properties 对象,并设置到全局配置中:
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 获取子元素属性
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 读取 resource 属性
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
// 读取 url 属性
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
// 不可均为空
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
// 加载指定路径文件,转为 properties
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
// 添加创建配置的附加属性
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
// 设置到全局配置中
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
解析 settings 元素
setteings 元素中的各子元素定义了 MyBatis 的运行时行为,例如:
<settings>
<!-- 缓存开关 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 懒加载开关 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false"/>
<!-- 允许自动生成主键 -->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<!-- 驼峰命名开关 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
...
</settings>
这些配置在 Configuration 类中都有对应的 setter 方法。settings 元素的解析方法对配置进行了验证:
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) {
if (context == null) {
return new Properties();
}
// 获取子元素配置
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
// 获取 Configuration 类的相关信息
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory);
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
// 验证对应的 setter 方法存在,保证配置是有效的
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
return props;
}
如果不存在对应的配置,会抛出 BuilderException 异常,如果自定义配置都是生效的,随后会调用 settingsElement 方法将这些运行时行为设置到全局配置中。
解析 typeAliases 元素
typeAliases 元素用于定义类别名:
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.wch.mybatis.User"/>
<typeAlias alias="User" type="com.wch.mybatis.User"/>
<typeAlias type="com.wch.mybatis.Item"/>
</typeAliases>
如果使用 package 元素注册别名,则对应包下的所有类都会注册到 TypeAliasRegistry 别名注册容器中;如果使用 typeAlias 元素,则会注册指定类到别名容器中。注册逻辑如下,如果没有指定别名,则优先从类的 Alias 注解获取别名,如果未在类上定义,则默认使用简单类名:
/**
* 注册指定包下所有类型别名
*
* @param packageName
*/
public void registerAliases(String packageName) {
registerAliases(packageName, Object.class);
}
/**
* 注册指定包下指定类型的别名
*
* @param packageName
* @param superType
*/
public void registerAliases(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
// 找出该包下superType所有的子类
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> typeSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> type : typeSet) {
// Ignore inner classes and interfaces (including package-info.java)
// Skip also inner classes. See issue #6
if (!type.isAnonymousClass() && !type.isInterface() && !type.isMemberClass()) {
registerAlias(type);
}
}
}
/**
* 注册类型别名,默认为简单类名,优先从 Alias 注解获取
*
* @param type
*/
public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) {
String alias = type.getSimpleName();
// 从Alias注解读取别名
Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class);
if (aliasAnnotation != null) {
alias = aliasAnnotation.value();
}
registerAlias(alias, type);
}
/**
* 注册类型别名
*
* @param alias 别名
* @param value 类型
*/
public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) {
if (alias == null) {
throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null");
}
// issue #748
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (typeAliases.containsKey(key) && typeAliases.get(key) != null && !typeAliases.get(key).equals(value)) {
throw new TypeException("The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + typeAliases.get(key).getName() + "'.");
}
typeAliases.put(key, value);
}
解析 plugins 元素
插件是 MyBatis 提供的扩展机制之一,通过添加自定义插件可以实现在 SQL 执行过程中的某个时机进行拦截。 plugins 元素用于定义调用拦截器:
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.wch.mybatis.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="name" value="ExamplePlugin"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
指定的 interceptor 需要实现 org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor 接口,在创建对象后被加到全局配置过滤器链中:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 获取 interceptor 属性
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
// 从子元素中读取属性配置
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 加载指定拦截器并创建实例
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 加入全局配置拦截器链
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
objectFactory、 objectWrapperFactory、reflectorFactory 元素的解析方式与 plugins 元素类似 ,指定的子类对象创建后被设置到全局对象中。
解析 environments 元素
在实际生产中,一个项目可能会分为多个不同的环境,通过配置enviroments 元素可以定义不同的数据环境,并在运行时使用指定的环境:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="" value=""/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="UNPOOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="prd">
...
</environment>
</environments>
在解析过程中,只有被 default 属性指定的数据环境才会被加载:
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
// 获取指定的数据源名
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
// 环境配置 id
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
// 加载指定环境配置
// 解析 transactionManager 元素并创建事务工厂实例
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
// 解析 dataSource 元素并创建数据源工厂实例
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
// 创建数据源
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
// 创建环境
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
// 将环境配置信息设置到全局配置中
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 解析 transactionManager 元素并创建事务工厂实例
*
* @param context
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 指定事务工厂类型
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// 从子元素读取属性配置
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 加载事务工厂并创建实例
TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory.");
}
/**
* 解析 dataSource 元素并创建数据源工厂实例
*
* @param context
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private DataSourceFactory dataSourceElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 指定数据源工厂类型
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// 从子元素读取属性配置
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 加载数据源工厂并创建实例
DataSourceFactory factory = (DataSourceFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a DataSourceFactory.");
}
解析 databaseIdProvider 元素
MyBatis 支持通过 databaseIdProvider 元素来指定支持的数据库的 databaseId,这样在映射配置文件中指定 databaseId 就能够与对应的数据源进行匹配:
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/>
<property name="DB2" value="db2"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle" />
</databaseIdProvider>
在根据指定类型解析出对应的 DatabaseIdProvider 后,MyBatis 会根据数据源获取对应的厂商信息:
private void databaseIdProviderElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider = null;
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// awful patch to keep backward compatibility
if ("VENDOR".equals(type)) {
type = "DB_VENDOR";
}
// 从子元素读取属性配置
Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 加载数据库厂商信息配置类并创建实例
databaseIdProvider = (DatabaseIdProvider) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
databaseIdProvider.setProperties(properties);
}
Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
if (environment != null && databaseIdProvider != null) {
// 获取数据库厂商标识
String databaseId = databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(environment.getDataSource());
configuration.setDatabaseId(databaseId);
}
}
因为 DB_VENDOR 被指定为 VendorDatabaseIdProvider 的别名,所以默认的获取厂商信息的逻辑如下,当通过 property 属性指定了数据库产品名则使用指定的名称,否则使用数据库元信息对应的产品名。
/**
* 根据数据源获取对应的厂商信息
*
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Override
public String getDatabaseId(DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("dataSource cannot be null");
}
try {
return getDatabaseName(dataSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
LogHolder.log.error("Could not get a databaseId from dataSource", e);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties p) {
this.properties = p;
}
/**
* 如果传入的属性配置包含当前数据库产品名,返回指定的值,否则返回数据库产品名
*
* @param dataSource
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
private String getDatabaseName(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
String productName = getDatabaseProductName(dataSource);
if (this.properties != null) {
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> property : properties.entrySet()) {
if (productName.contains((String) property.getKey())) {
return (String) property.getValue();
}
}
// no match, return null
return null;
}
return productName;
}
/**
* 获取数据库产品名
*
* @param dataSource
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
private String getDatabaseProductName(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Connection con = null;
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
DatabaseMetaData metaData = con.getMetaData();
return metaData.getDatabaseProductName();
} finally {
if (con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// ignored
}
}
}
}
解析 typeHandlers 元素
typeHandlers 元素用于配置自定义类型转换器:
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="com.wch.mybatis.ExampleTypeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>
如果配置的是 package 元素,则会将包下的所有类注册为类型转换器;如果配置的是 typeHandler 元素,则会根据 javaType、jdbcType、handler 属性注册类型转换器。
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 注册指定包下的类作为类型转换器,如果声明了 MappedTypes 注解则注册为指定 java 类型的转换器
String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage);
} else {
// 获取相关属性
String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler");
// 加载指定 java 类型类对象
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName);
// 加载指定 JDBC 类型并创建实例
JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName);
// 加载指定类型转换器类对象
Class<?> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName);
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
// 注册类型转换器
if (jdbcType == null) {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass);
}
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass);
}
}
}
}
}
解析 mappers 元素
mappers 元素用于定义 Mapper 映射文件和 Mapper 调用接口:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/wch/mybatis/UserMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file://mappers/ItemMapper.xml"/>
<mapper class="com.wch.mybatis.UserMapper"/>
<package name="com.wch.mybatis.mappers"/>
</mappers>
如果定义的是 mapper 元素并指定了 class 属性,或定义了 package 元素,则会将指定类型在 MapperRegistry 中注册为 Mapper 接口,并使用 MapperAnnotationBuilder 对接口方法进行解析;如果定义的是 mapper 元素并指定了 resource、或 url 属性,则会使用 XMLMapperBuilder 解析。对于 Mapper 接口和映射文件将在下一章进行分析。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 注册指定包名下的类为 Mapper 接口
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
// 加载指定资源
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 加载指定 Mapper 文件并解析
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
// 加载指定 URL
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
// 加载指定 Mapper 文件并解析
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// 注册指定类为 Mapper 接口
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
总结
XMLConfigBuilder 是 XML 配置解析的入口,通常 MyBatis 启动时会使用此类解析配置文件获取运行时行为。
- org.apache.ibatis.builder.BaseBuilder:为 MyBatis 初始化过程提供一系列工具方法。如别名转换、类型转换、类加载等。
- org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder:XML 配置解析入口。
- org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration:MyBatis 全局配置,包括运行行为、类型容器、别名容器、注册 Mapper、注册 statement 等。
- org.apache.ibatis.mapping.VendorDatabaseIdProvider:根据数据源获取对应的厂商信息。
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.