CH03-基础支持模块
类型转换
JDBC 规范定义的数据类型与 Java 数据类型并不是完全对应的,所以在 PrepareStatement 为 SQL 语句绑定参数时,需要从 Java 类型转为 JDBC 类型;而从结果集中获取数据时,则需要将 JDBC 类型转为 Java 类型。
类型转换操作
MyBatis 中的所有类型转换器都继承自 BaseTypeHandler 抽象类,此类实现了 TypeHandler 接口。接口中定义了 1 个向 PreparedStatement 对象中设置参数的方法和 3 个从结果集中取值的方法:
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
/**
* 为PreparedStatement对象设置参数
*
* @param ps SQL 预编译对象
* @param i 参数索引
* @param parameter 参数值
* @param jdbcType 参数 JDBC类型
* @throws SQLException
*/
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
/**
* 根据列名从结果集中取值
*
* @param rs 结果集
* @param columnName 列名
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
/**
* 根据索引从结果集中取值
* @param rs 结果集
* @param columnIndex 索引
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
/**
* 根据索引从存储过程函数中取值
*
* @param cs 存储过程对象
* @param columnIndex 索引
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
BaseTypeHandler 及其实现
BaseTypeHandler 实现了 TypeHandler 接口,针对 null 和异常处理做了封装,但是具体逻辑封装成 4 个抽象方法仍交由相应的类型转换器子类实现,以 IntegerTypeHandler 为例,其实现如下:
public class IntegerTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Integer> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Integer parameter, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
ps.setInt(i, parameter);
}
@Override
public Integer getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)
throws SQLException {
int result = rs.getInt(columnName);
// 如果列值为空值返回控制否则返回原值
return result == 0 && rs.wasNull() ? null : result;
}
@Override
public Integer getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
int result = rs.getInt(columnIndex);
return result == 0 && rs.wasNull() ? null : result;
}
@Override
public Integer getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
int result = cs.getInt(columnIndex);
return result == 0 && cs.wasNull() ? null : result;
}
}
其实现主要是调用 JDBC API 设置查询参数或取值,并对 null 等特定情况做特殊处理。
类型转换注册器
TypeHandlerRegistry 是 TypeHandler 的注册类,在其无参构造方法中维护了 JavaType、JdbcType 和 TypeHandler 的关系。其主要使用的容器如下:
/**
* JdbcType - TypeHandler对象
* 用于将Jdbc类型转为Java类型
*/
private final Map<JdbcType, TypeHandler<?>> jdbcTypeHandlerMap = new EnumMap<>(JdbcType.class);
/**
* JavaType - JdbcType - TypeHandler对象
* 用于将Java类型转为指定的Jdbc类型
*/
private final Map<Type, Map<JdbcType, TypeHandler<?>>> typeHandlerMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* TypeHandler类型 - TypeHandler对象
* 注册所有的TypeHandler类型
*/
private final Map<Class<?>, TypeHandler<?>> allTypeHandlersMap = new HashMap<>();
别名注册
别名转换器注册
TypeAliasRegistry 提供了多种方式用于为 Java 类型注册别名。包括直接指定别名、注解指定别名、为指定包下类型注册别名:
/**
* 注册指定包下所有类型别名
*
* @param packageName
*/
public void registerAliases(String packageName) {
registerAliases(packageName, Object.class);
}
/**
* 注册指定包下指定类型的别名
*
* @param packageName
* @param superType
*/
public void registerAliases(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
// 找出该包下superType所有的子类
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> typeSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> type : typeSet) {
// Ignore inner classes and interfaces (including package-info.java)
// Skip also inner classes. See issue #6
if (!type.isAnonymousClass() && !type.isInterface() && !type.isMemberClass()) {
registerAlias(type);
}
}
}
/**
* 注册类型别名,默认为简单类名,优先从Alias注解获取
*
* @param type
*/
public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) {
String alias = type.getSimpleName();
// 从Alias注解读取别名
Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class);
if (aliasAnnotation != null) {
alias = aliasAnnotation.value();
}
registerAlias(alias, type);
}
/**
* 注册类型别名
*
* @param alias 别名
* @param value 类型
*/
public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) {
if (alias == null) {
throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null");
}
// issue #748
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (typeAliases.containsKey(key) && typeAliases.get(key) != null && !typeAliases.get(key).equals(value)) {
throw new TypeException("The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + typeAliases.get(key).getName() + "'.");
}
typeAliases.put(key, value);
}
/**
* 注册类型别名
* @param alias 别名
* @param value 指定类型全名
*/
public void registerAlias(String alias, String value) {
try {
registerAlias(alias, Resources.classForName(value));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error registering type alias " + alias + " for " + value + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
所有别名均注册到名为 typeAliases 的容器中。TypeAliasRegistry 的无参构造方法默认为一些常用类型注册了别名,如 Integer、String、byte[] 等。
日志配置
MyBatis 支持与多种日志工具集成,包括 Slf4j、log4j、log4j2、commons-logging 等。这些第三方工具类对应日志的实现各有不同,MyBatis 通过适配器模式抽象了这些第三方工具的集成过程,按照一定的优先级选择具体的日志工具,并将真正的日志实现委托给选择的日志工具。
日志适配接口
Log 接口是 MyBatis 的日志适配接口,支持 trace、debug、warn、error 四种级别。
日志工厂
LogFactory 负责对第三方日志工具进行适配,在类加载时会通过静态代码块按顺序选择合适的日志实现。
static {
// 按顺序加载日志实现,如果有某个第三方日志实现可以成功加载,则不继续加载其它实现
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useSlf4jLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useCommonsLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4J2Logging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4JLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useJdkLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useNoLogging);
}
/**
* 初始化 logConstructor
*
* @param runnable
*/
private static void tryImplementation(Runnable runnable) {
if (logConstructor == null) {
try {
// 同步执行
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}
/**
* 配置第三方日志实现适配器
*
* @param implClass
*/
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
tryImplementation 按顺序加载第三方日志工具的适配实现,如 Slf4j 的适配器 Slf4jImpl:
public Slf4jImpl(String clazz) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(clazz);
if (logger instanceof LocationAwareLogger) {
try {
// check for slf4j >= 1.6 method signature
logger.getClass().getMethod("log", Marker.class, String.class, int.class, String.class, Object[].class, Throwable.class);
log = new Slf4jLocationAwareLoggerImpl((LocationAwareLogger) logger);
return;
} catch (SecurityException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
// fail-back to Slf4jLoggerImpl
}
}
// Logger is not LocationAwareLogger or slf4j version < 1.6
log = new Slf4jLoggerImpl(logger);
}
如果 Slf4jImpl 能成功执行构造方法,则 LogFactory 的 logConstructor 被成功赋值,MyBatis 就找到了合适的日志实现,可以通过 getLog 方法获取 Log 对象。
JDBC 日志代理
org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc 包提供了 Connection、PrepareStatement、Statement、ResultSet 类中的相关方法执行的日志记录代理。BaseJdbcLogger 在创建时整理了 PreparedStatement 执行的相关方法名,并提供容器保存列值:
/**
* PreparedStatement 接口中的 set* 方法名称集合
*/
protected static final Set<String> SET_METHODS;
/**
* PreparedStatement 接口中的 部分执行方法
*/
protected static final Set<String> EXECUTE_METHODS = new HashSet<>();
/**
* 列名-列值
*/
private final Map<Object, Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 列名集合
*/
private final List<Object> columnNames = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 列值集合
*/
private final List<Object> columnValues = new ArrayList<>();
static {
SET_METHODS = Arrays.stream(PreparedStatement.class.getDeclaredMethods())
.filter(method -> method.getName().startsWith("set"))
.filter(method -> method.getParameterCount() > 1)
.map(Method::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("execute");
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("executeUpdate");
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("executeQuery");
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("addBatch");
}
protected void setColumn(Object key, Object value) {
columnMap.put(key, value);
columnNames.add(key);
columnValues.add(value);
}
ConnectionLogger、PreparedStatementLogger、StatementLogger、ResultSetLogger 都继承自 BaseJdbcLogger,并实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,在运行时通过 JDK 动态代理实现代理类,针对相关方法执行打印日志。如下是 ConnectionLogger 对 InvocationHandler 接口的实现:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params)
throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if ("prepareStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
// 执行创建PreparedStatement方法,使用PreparedStatementLogger代理
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else if ("prepareCall".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else if ("createStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
Statement stmt = (Statement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = StatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else {
return method.invoke(connection, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
如果执行 prepareStatement 方法创建 PrepareStatement 对象,则会使用动态代理创建 PreparedStatementLogger 对象增强原有对象。在 PreparedStatementLogger 的代理逻辑中,如果执行的是 executeQuery 或 getResultSet 方法,其返回值 ResultSet 也会包装为 ResultSetLogger 作为代理,其代理逻辑为如果执行 ResultSet 的 next 方法,会打印结果集的行。
资源加载
Resources 与 ClassLoaderWrapper
MyBatis 提供工具类 Resources 用于工具加载,其底层是通过 ClassLoaderWrapper 实现的。ClassLoaderWrapper 组合了一系列的 ClassLoader:
ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new ClassLoader[]{
// 指定 ClassLoader
classLoader,
// 默认 ClassLoader,默认为 null
defaultClassLoader,
// 当前线程对应的 ClassLoader
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
// 当前类对应的 ClassLoader
getClass().getClassLoader(),
// 默认为 SystemClassLoader
systemClassLoader};
}
当加载资源时会按组合的 ClassLoader 顺序依次尝试加载资源,例如 classForName 方法的实现:
Class<?> classForName(String name, ClassLoader[] classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 按组合顺序依次加载
for (ClassLoader cl : classLoader) {
if (null != cl) {
try {
// 类加载
Class<?> c = Class.forName(name, true, cl);
if (null != c) {
return c;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// we'll ignore this until all classloaders fail to locate the class
}
}
}
throw new ClassNotFoundException("Cannot find class: " + name);
}
加载指定包下的类
ResolverUtil 的 find 方法用于按条件加载指定包下的类。
public ResolverUtil<T> find(Test test, String packageName) {
// 包名.替换为/
String path = getPackagePath(packageName);
try {
// 虚拟文件系统加载文件路径
List<String> children = VFS.getInstance().list(path);
for (String child : children) {
if (child.endsWith(".class")) {
// 如果指定class文件符合条件,加入容器
addIfMatching(test, child);
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error("Could not read package: " + packageName, ioe);
}
return this;
}
ResolverUtil 还提供了一个内部接口 Test 用于判断指定类型是否满足条件,在 ResolverUtil 有两个默认实现:IsA 用于判断是否为指定类型的子类;AnnotatedWith 用于判断类上是否有指定注解。
/**
* A Test that checks to see if each class is assignable to the provided class. Note
* that this test will match the parent type itself if it is presented for matching.
*
* 判断是否为子类
*/
public static class IsA implements Test {
private Class<?> parent;
/** Constructs an IsA test using the supplied Class as the parent class/interface. */
public IsA(Class<?> parentType) {
this.parent = parentType;
}
/** Returns true if type is assignable to the parent type supplied in the constructor. */
@Override
public boolean matches(Class<?> type) {
return type != null && parent.isAssignableFrom(type);
}
}
/**
* A Test that checks to see if each class is annotated with a specific annotation. If it
* is, then the test returns true, otherwise false.
*
* 判断类上是否有指定注解
*/
public static class AnnotatedWith implements Test {
private Class<? extends Annotation> annotation;
/** Constructs an AnnotatedWith test for the specified annotation type. */
public AnnotatedWith(Class<? extends Annotation> annotation) {
this.annotation = annotation;
}
/** Returns true if the type is annotated with the class provided to the constructor. */
@Override
public boolean matches(Class<?> type) {
return type != null && type.isAnnotationPresent(annotation);
}
}
如果要加载的类复合条件,则将加载的类对象加入容器。
protected void addIfMatching(Test test, String fqn) {
try {
String externalName = fqn.substring(0, fqn.indexOf('.')).replace('/', '.');
ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checking to see if class " + externalName + " matches criteria [" + test + "]");
}
// 加载类
Class<?> type = loader.loadClass(externalName);
if (test.matches(type)) {
// 符合条件,加入容器
matches.add((Class<T>) type);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("Could not examine class '" + fqn + "'" + " due to a " +
t.getClass().getName() + " with message: " + t.getMessage());
}
}
数据源实现
MyBatis 提供了自己的数据源实现,分别为非池化数据源 UnpooledDataSource 和池化数据源 PooledDataSource。两个数据源都实现了 javax.sql.DataSource 接口并分别由 UnpooledDataSourceFactory 和 PooledDataSourceFactory 工厂类创建。两个工厂类又都实现了 DataSourceFactory 接口。
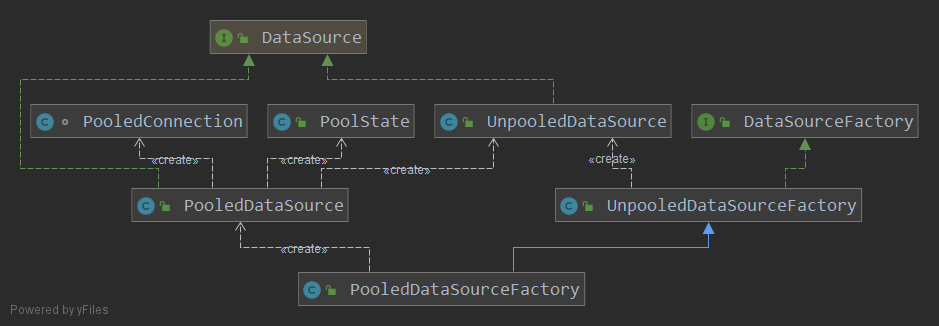
DataSourceFactory 实现
UnpooledDataSourceFactory 实现了 DataSourceFactory 接口的 setProperties 和 getDataSource 方法,分别用于在创建数据源工厂后配置数据源属性和获取数据源,PooledDataSourceFactory 继承了其实现:
public UnpooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
/**
* 创建数据源工厂后配置数据源属性
*
* @param props
*/
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
Properties driverProperties = new Properties();
// 数据源对象信息
MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource);
for (Object key : properties.keySet()) {
String propertyName = (String) key;
if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) {
// 数据源驱动相关属性
String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName);
driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value);
} else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) {
// 属性在数据源类中有相应的set方法
String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName);
// 转换类型
Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value);
// 反射赋值
metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue);
} else {
throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName);
}
}
if (driverProperties.size() > 0) {
metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties);
}
}
/**
* 获取数据源
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
非池化数据源
UnpooledDataSource 在静态语句块中从数据源驱动管理器 DriverManager 获取所有已注册驱动并放入本地容器:
static {
// 从数据库驱动类中获取所有驱动
Enumeration<Driver> drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
此数据源获取连接的实现为调用 doGetConnection 方法,每次获取连接时先校验当前驱动是否注册,如果已注册则直接创建新连接,并配置自动提交属性和默认事务隔离级别:
/**
* 获取连接
*
* @param properties
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
// 校验当前驱动是否注册,如果未注册,加载驱动并注册
initializeDriver();
// 获取数据库连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
// 配置自动提交和默认事务隔离级别属性
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}
/**
* 校验当前驱动是否注册
*
* @throws SQLException
*/
private synchronized void initializeDriver() throws SQLException {
if (!registeredDrivers.containsKey(driver)) {
// 当前驱动还未注册
Class<?> driverType;
try {
// 加载驱动类
if (driverClassLoader != null) {
driverType = Class.forName(driver, true, driverClassLoader);
} else {
driverType = Resources.classForName(driver);
}
// DriverManager requires the driver to be loaded via the system ClassLoader.
// http://www.kfu.com/~nsayer/Java/dyn-jdbc.html
Driver driverInstance = (Driver)driverType.newInstance();
// 注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new DriverProxy(driverInstance));
registeredDrivers.put(driver, driverInstance);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException("Error setting driver on UnpooledDataSource. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
/**
* 配置自动提交和默认事务隔离级别属性
*
* @param conn
* @throws SQLException
*/
private void configureConnection(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
if (autoCommit != null && autoCommit != conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
if (defaultTransactionIsolationLevel != null) {
conn.setTransactionIsolation(defaultTransactionIsolationLevel);
}
}
池化数据源
数据库连接的创建是十分耗时的,在高并发环境下,频繁地创建和关闭连接会为系统带来很大的开销。而使用连接池实现对数据库连接的重用可以显著提高性能,避免反复创建连接。MyBatis 实现的连接池包含了维护连接队列、创建和保存连接、归还连接等功能。
池化连接
PooledConnection 是 MyBatis 的池化连接实现。其构造方法中传入了驱动管理器创建的真正连接,并通过 JDK 动态代理创建了连接的代理对象:
public PooledConnection(Connection connection, PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.hashCode = connection.hashCode();
// 真正的数据库连接
this.realConnection = connection;
// 数据源对象
this.dataSource = dataSource;
// 连接创建时间
this.createdTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 连接上次使用时间
this.lastUsedTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 数据源有效标志
this.valid = true;
// 创建连接代理
this.proxyConnection = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this);
}
连接代理的逻辑如下,如果执行 close 方法,并不会真正的关闭连接,而是当作空闲连接交给数据源处理,根据连接池的状态选择将连接放入空闲队列或关闭连接;如果执行其它方法,则会判断当前连接是否有效,如果是无效连接会抛出异常:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
// 调用连接关闭方法代理逻辑:处理空闲连接,放入空闲队列或关闭
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
}
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// issue #579 toString() should never fail
// throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime
// 执行其它方法,验证连接是否有效,如果是无效连接,抛出异常
checkConnection();
}
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
连接池状态
PoolState 维护了数据库连接池状态。其内部维护了两个容器,分别为空闲连接集合和活跃连接集合。
/**
* 空闲连接集合
*/
protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 活跃连接集合
*/
protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<>();
获取连接
池化数据源 PooledDataSource 是依赖 UnpooledDataSource 实现的。其获取连接的方式是调用 popConnection 方法。在获取连接池同步锁后按照以下顺序尝试获取可用连接:
- 从空闲队列获取连接
- 活跃连接池未满,创建新连接
- 检查最早的活跃连接是否超时
- 等待释放连接
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
// 等待连接标志
boolean countedWait = false;
// 待获取的池化连接
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
while (conn == null) {
// 循环获取连接
synchronized (state) {
// 获取连接池的同步锁
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
// Pool has available connection 连接池中有空闲连接
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
// Pool does not have available connection 连接池无可用连接
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// Can create new connection 活跃连接数小于设定的最大连接数,创建新的连接(从驱动管理器创建新的连接)
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Cannot create new connection 活跃连接数到达最大连接数
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
// 查询最早入队的活跃连接使用时间(即使用时间最长的活跃连接使用时间)
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// Can claim overdue connection 超出活跃连接最大使用时间
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
// 超时连接累计使用时长
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
// 活跃连接队列移除当前连接
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
try {
// 创建的连接未自动提交,执行回滚
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happened.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not interrupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competition for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
// 包装新的池化连接
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 设置原连接无效
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Must wait
try {
// 存活连接有效
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 释放锁等待连接,{@link PooledDataSource#pushConnection} 如果有连接空闲,会唤醒等待
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
// 记录等待时长
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
// ping to server and check the connection is valid or not
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 连接有效
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
// 非自动提交的连接,回滚上次任务
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
// 设置连接新的使用时间
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 添加到活跃连接集合队尾
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
// 连接请求次数+1
state.requestCount++;
// 请求连接花费的时间
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
// 未获取到连接
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
// 因为没有空闲连接导致获取连接失败次数+1
state.badConnectionCount++;
// 本次请求获取连接失败数+1
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
// 超出获取连接失败的可容忍次数,抛出异常
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
如果暂时获取不到可用连接,则当前线程进入等待,等待新的空闲连接产生唤醒等待或等待超时后重新尝试获取连接。当尝试次数到达指定上限,会抛出异常跳出等待。
判断连接有效性
如果可以从连接池中获取连接,会调用 PooledConnection#isValid 方法判断连接是否有效,其逻辑为 PooledConnection 对象自身维护的标志有效且连接存活。判断连接存活的实现如下:
protected boolean pingConnection(PooledConnection conn) {
boolean result = true;
try {
// 连接是否关闭
result = !conn.getRealConnection().isClosed();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is BAD: " + e.getMessage());
}
result = false;
}
if (result) {
if (poolPingEnabled) {
// 使用语句检测连接是否可用开关开启
if (poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor >= 0 && conn.getTimeElapsedSinceLastUse() > poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor) {
// 距上次连接使用经历时长超过设置的阈值
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Testing connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " ...");
}
// 验证连接是否可用
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
try (Statement statement = realConn.createStatement()) {
statement.executeQuery(poolPingQuery).close();
}
if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) {
// 未自动提交执行回滚
realConn.rollback();
}
result = true;
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is GOOD!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Execution of ping query '" + poolPingQuery + "' failed: " + e.getMessage());
try {
// 抛出异常,连接不可用,关闭连接
conn.getRealConnection().close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
//ignore
}
result = false;
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is BAD: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
默认调用 Connection#isClosed 方法判断连接是否存活,如果连接存活,则可以选择执行 SQL 语句来进一步判断连接的有效性。是否进一步验证、验证使用的 SQL 语句、验证的时间条件,都是可配置的。
处理空闲连接
在池化连接的代理连接执行关闭操作时,会转为对空闲连接的处理,其实现逻辑如下:
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
synchronized (state) {
// 获取连接池状态同步锁,活跃连接队列移除当前连接
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 连接有效
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
// 空闲连接数小于最大空闲连接数,累计连接使用时长
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
// 未自动提交连接回滚上次事务
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 包装成新的代理连接
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
// 将新连接放入空闲队列
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
// 设置相关统计时间戳
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 老连接设置失效
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
// 唤醒等待连接的线程,通知有新连接可以使用
state.notifyAll();
} else {
// 空闲连接数达到最大空闲连接数
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
// 未自动提交连接回滚上次事务
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 关闭多余的连接
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
// 连接设置失效
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
// 连接无效次数+1
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
如果当前空闲连接数小于最大空闲连接数,则将空闲连接放入空闲队列,否则关闭连接。
处理配置变更
在相关配置变更后,MyBatis 会调用 forceCloseAll 关闭连接池中所有存活的连接:
public void forceCloseAll() {
synchronized (state) {
// 获取连接池状态同步锁
expectedConnectionTypeCode = assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword());
for (int i = state.activeConnections.size(); i > 0; i--) {
try {
// 移除活跃连接
PooledConnection conn = state.activeConnections.remove(i - 1);
// 原连接置为无效
conn.invalidate();
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) {
// 未提交连接回滚当前事务
realConn.rollback();
}
// 关闭连接
realConn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
for (int i = state.idleConnections.size(); i > 0; i--) {
try {
// 移除空闲连接
PooledConnection conn = state.idleConnections.remove(i - 1);
// 原连接置为无效
conn.invalidate();
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) {
// 未提交连接回滚当前事务
realConn.rollback();
}
// 关闭连接
realConn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections.");
}
}
缓存实现
Cache 是 MyBatis 的缓存抽象接口,其要求实现如下方法:
public interface Cache {
/**
* 缓存对象 id
*
* @return The identifier of this cache
*/
String getId();
/**
* 设置缓存
*
* @param key Can be any object but usually it is a {@link CacheKey}
* @param value The result of a select.
*/
void putObject(Object key, Object value);
/**
* 获取缓存
*
* @param key The key
* @return The object stored in the cache.
*/
Object getObject(Object key);
/**
* 移除缓存
*
* @param key The key
* @return Not used
*/
Object removeObject(Object key);
/**
* 清空缓存
*
* Clears this cache instance.
*/
void clear();
/**
* Optional. This method is not called by the core.
* 获取缓存项数量
*
* @return The number of elements stored in the cache (not its capacity).
*/
int getSize();
/**
* 获取读写锁
*
* @return A ReadWriteLock
*/
ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock();
}
基础实现
PerpetualCache 类是基础实现类,核心是基于 HashMap 作为缓存维护容器。在此基础上,MyBatis 实现了多种缓存装饰器,用于满足不同的需求。
缓存装饰器
同步操作
SynchronizedCache 针对缓存操作方法加上了 synchronized 关键字用于进行同步操作。
阻塞操作
BlockingCache 在执行获取缓存操作时对 key 加锁,直到写缓存后释放锁,保证了相同 key 同一时刻只有一个线程执行数据库操作,其它线程在缓存层阻塞。
/**
* 写缓存完成后释放锁
*/
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
try {
delegate.putObject(key, value);
} finally {
releaseLock(key);
}
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// 获取锁
acquireLock(key);
Object value = delegate.getObject(key);
if (value != null) {
// 缓存不为空则释放锁,否则继续持有锁,在进行数据库操作后写缓存释放锁
releaseLock(key);
}
return value;
}
/**
* 删除指定 key 对应的缓存,并释放锁
*
* @param key The key
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
// despite of its name, this method is called only to release locks
releaseLock(key);
return null;
}
/**
* 获取已有的锁或创建新锁
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
private ReentrantLock getLockForKey(Object key) {
return locks.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ReentrantLock());
}
/**
* 根据 key 获取锁
*
* @param key
*/
private void acquireLock(Object key) {
Lock lock = getLockForKey(key);
if (timeout > 0) {
try {
boolean acquired = lock.tryLock(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!acquired) {
throw new CacheException("Couldn't get a lock in " + timeout + " for the key " + key + " at the cache " + delegate.getId());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new CacheException("Got interrupted while trying to acquire lock for key " + key, e);
}
} else {
lock.lock();
}
}
/**
* 释放锁
*
* @param key
*/
private void releaseLock(Object key) {
ReentrantLock lock = locks.get(key);
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
日志记录
LoggingCache 是缓存日志装饰器。查询缓存时会记录查询日志并统计命中率。
/**
* 查询缓存时记录查询日志并统计命中率
*
* @param key The key
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// 查询数+1
requests++;
final Object value = delegate.getObject(key);
if (value != null) {
// 命中数+1
hits++;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Cache Hit Ratio [" + getId() + "]: " + getHitRatio());
}
return value;
}
定时清理
ScheduledCache 是缓存定时清理装饰器。在执行缓存相关操作时会根据设置的时间间隔判断是否需要清除全部的缓存。
/**
* 操作缓存时判断是否需要清除所有缓存。
*
* @return
*/
private boolean clearWhenStale() {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - lastClear > clearInterval) {
clear();
return true;
}
return false;
}
序列化与反序列化
SerializedCache 是缓存序列化装饰器,其在写入时会将值序列化成对象流,并在读取时进行反序列化。
事务操作
TransactionalCache 是事务缓存装饰器。在事务提交后再将缓存写入,如果发生回滚则不写入。
先进先出
FifoCache 是先进先出缓存装饰器。其按写缓存顺序维护了一个缓存 key 队列,如果缓存项超出指定大小,则删除最先入队的缓存。
/**
* 按写缓存顺序维护缓存 key 队列,缓存项超出指定大小,删除最先入队的缓存
*
* @param key
*/
private void cycleKeyList(Object key) {
keyList.addLast(key);
if (keyList.size() > size) {
Object oldestKey = keyList.removeFirst();
delegate.removeObject(oldestKey);
}
}
最近最久未使用
LruCache 是缓存最近最久未使用装饰器。其基于 LinkedHashMap 维护了 key 的 LRU 顺序。
public void setSize(final int size) {
// LinkedHashMap 在执行 get 方法后会将对应的 entry 移到队尾来维护使用顺序
keyMap = new LinkedHashMap<Object, Object>(size, .75F, true) {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4267176411845948333L;
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Object, Object> eldest) {
boolean tooBig = size() > size;
if (tooBig) {
// 超出缓存项数量限制,获取最近最久未使用的key
eldestKey = eldest.getKey();
}
return tooBig;
}
};
}
/**
* 更新缓存后检查是否需要删除最近最久未使用的缓存项
*/
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
delegate.putObject(key, value);
cycleKeyList(key);
}
private void cycleKeyList(Object key) {
keyMap.put(key, key);
if (eldestKey != null) {
delegate.removeObject(eldestKey);
eldestKey = null;
}
}
软引用缓存
SoftCache 是缓存软引用装饰器,其使用了软引用 + 强引用队列的方式维护缓存。在写缓存操作中,写入的数据其实时缓存项的软引用包装对象,在 Full GC 时,如果没有一个强引用指向被包装的缓存项或缓存值,并且系统内存不足,缓存项就会被 GC,被回收对象进入指定的引用队列。
/**
* 引用队列,用于记录已经被 GC 的 SoftEntry 对象
*/
private final ReferenceQueue<Object> queueOfGarbageCollectedEntries;
/**
* 写入缓存。
* 不直接写缓存的值,而是写入缓存项对应的软引用
*/
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
removeGarbageCollectedItems();
// 在 Full GC 时,如果没有一个强引用指向被包装的缓存项或缓存值,并且系统内存不足,缓存项就会被回收,被回收对象进入指定的引用队列
delegate.putObject(key, new SoftEntry(key, value, queueOfGarbageCollectedEntries));
}
/**
* 查询已被 GC 的软引用,删除对应的缓存项
*/
private void removeGarbageCollectedItems() {
SoftEntry sv;
while ((sv = (SoftEntry) queueOfGarbageCollectedEntries.poll()) != null) {
delegate.removeObject(sv.key);
}
}
/**
* 封装软引用对象
*/
private static class SoftEntry extends SoftReference<Object> {
private final Object key;
SoftEntry(Object key, Object value, ReferenceQueue<Object> garbageCollectionQueue) {
// 声明 value 为软引用对象
super(value, garbageCollectionQueue);
// key 为强引用
this.key = key;
}
}
在读取缓存时,如果软引用被回收,则删除对应的缓存项;否则将缓存项放入一个强引用队列中,该队列会将最新读取的缓存项放入队首,使得真正的缓存项有了强引用指向,其软引用包装就不会被垃圾回收。队列有数量限制,当超出限制时会删除队尾的缓存项。
/**
* 获取缓存。
* 如果软引用被回收则删除对应的缓存项,如果未回收则加入到有数量限制的 LRU 队列中
*
* @param key The key
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
Object result = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // assumed delegate cache is totally managed by this cache
SoftReference<Object> softReference = (SoftReference<Object>) delegate.getObject(key);
if (softReference != null) {
result = softReference.get();
if (result == null) {
// 软引用已经被回收,删除对应的缓存项
delegate.removeObject(key);
} else {
// 如果未被回收,增将软引用加入到 LRU 队列
// See #586 (and #335) modifications need more than a read lock
synchronized (hardLinksToAvoidGarbageCollection) {
// 将对应的软引用
hardLinksToAvoidGarbageCollection.addFirst(result);
if (hardLinksToAvoidGarbageCollection.size() > numberOfHardLinks) {
// 超出数量限制,删除最近最久未使用的软引用对象
hardLinksToAvoidGarbageCollection.removeLast();
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
弱引用缓存
WeakCache 是缓存弱引用装饰器,使用弱引用 + 强引用队列的方式维护缓存,其实现方式与 SoftCache 是一致的。
Binding 模块
为了避免因拼写等错误导致在运行期才发现执行方法找不到对应的 SQL 语句,MyBatis 使用 Binding 模块在启动时对执行方法校验,如果找不到对应的语句,则会抛出 BindingException。
MyBatis 一般将执行数据库操作的方法所在的接口称为 Mapper,MapperRegistry 用来注册 Mapper 接口类型与其代理创建工厂的映射,其提供 addMapper 和 addMappers 接口用于注册。Mapper 接口代理工厂是通过 MapperProxyFactory 创建,创建过程依赖 MapperProxy 提供的 JDK 动态代理:
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
/**
* 使用 Mapper 代理封装 SqlSession 相关操作
*
* @param sqlSession
* @return
*/
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
MapperProxy 的代理逻辑如下,在 Mapper 接口中的方法真正执行时,会为指定的非 default 方法创建方法信息和 SQL 执行信息缓存:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Object中的方法,直接执行
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
// 当前方法是接口中的非abstract、非static的public方法,即高版本JDK中的default方法
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 缓存 Mapper接口 对应的方法和 SQL 执行信息
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 执行 SQL
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
/**
* 缓存 Mapper接口 对应的方法和 SQL 执行信息
*
* @param method
* @return
*/
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
缓存通过 MapperMethod 类来保存,其构造方法创建了 SqlCommand 和 MethodSignature 对象。
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
// SQL 执行信息
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
// 获取方法参数和返回值相关信息
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
SqlCommand 会根据接口和方法名找到对应的 SQL statement 对象:
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,
Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
// statementId 为接口名与方法名组合
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
// 配置中存在此 statementId,返回对应的 statement
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
// 此方法就是在对应接口中声明的
return null;
}
// 递归查找父类
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
而 MethodSignature 会获取方法相关信息,如返回值类型、是否返回 void、是否返回多值等。对于 Param 注解的解析也会保存下来(MyBatis 使用 Param 注解重置参数名)。
总结
MyBatis 提供了一系列工具和实现,用于为整个框架提供基础支持。
- 类型转换
- org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler:类型转换器接口,抽象 JDBC 类型和 Java 类型互转逻辑。
- org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler:TypeHandler 的抽象实现,针对 null 和异常处理做了封装,具体逻辑仍由相应的类型转换器实现。
- org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry:TypeHandler 注册类,维护 JavaType、JdbcType 和 TypeHandler 关系。
- 别名注册
- org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeAliasRegistry:别名注册类。注册常用类型的别名,并提供多种注册别名的方式。
- 日志配置
- org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log:MyBatis 日志适配接口,支持 trace、debug、warn、error 四种级别。
- org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory:MyBatis 日志工厂,负责适配第三方日志实现。
- org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc:SQL 执行日志工具包,针对执行 Connection、PrepareStatement、Statement、ResultSet 类中的相关方法,提供日志记录工具。
- 资源加载
- org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources:MyBatis 封装的资源加载工具类。
- org.apache.ibatis.io.ClassLoaderWrapper:资源加载底层实现。组合多种 ClassLoader 按顺序尝试加载资源。
- org.apache.ibatis.io.ResolverUtil:按条件加载指定包下的类。
- 数据源实现
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.DataSourceFactory:数据源创建工厂接口。
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.unpooled.UnpooledDataSourceFactory:非池化数据源工厂。
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSourceFactory:池化数据源工厂。
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.unpooled.UnpooledDataSource:非池化数据源。
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource:池化数据源。
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledConnection:池化连接。
- org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PoolState:连接池状态。
- 事务实现
- org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction:事务抽象接口
- org.apache.ibatis.session.TransactionIsolationLevel:事务隔离级别。
- org.apache.ibatis.transaction.TransactionFactory:事务创建工厂抽象接口。
- org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction:封装 JDBC 数据库事务操作。
- org.apache.ibatis.transaction.managed.ManagedTransaction:数据库事务操作依赖外部管理。
- 缓存实现
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache:缓存抽象接口。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache:使用 HashMap 作为缓存实现容器的 Cache 基本实现。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.BlockingCache:缓存阻塞装饰器。保证相同 key 同一时刻只有一个线程执行数据库操作,其它线程在缓存层阻塞。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.FifoCache:缓存先进先出装饰器。按写缓存顺序维护缓存 key 队列,缓存项超出指定大小,删除最先入队的缓存。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LruCache:缓存最近最久未使用装饰器。基于 LinkedHashMap 维护了 key 的 LRU 顺序。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LoggingCache:缓存日志装饰器。查询缓存时记录查询日志并统计命中率。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.ScheduledCache:缓存定时清理装饰器。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.SerializedCache:缓存序列化装饰器。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.SynchronizedCache:缓存同步装饰器。在缓存操作方法上使用 synchronized 关键字同步。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.TransactionalCache:事务缓存装饰器。在事务提交后再将缓存写入,如果发生回滚则不写入。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.SoftCache:缓存软引用装饰器。使用软引用 + 强引用队列的方式维护缓存。
- org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.WeakCache:缓存弱引用装饰器。使用弱引用 + 强引用队列的方式维护缓存。
- Binding
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry: Mapper 接口注册类,管理 Mapper 接口类型和其代理创建工厂的映射。
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxyFactory:Mapper 接口代理创建工厂。
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy:Mapper 接口方法代理逻辑,封装 SqlSession 相关操作。
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod:封装 Mapper 接口对应的方法和 SQL 执行信息。
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.